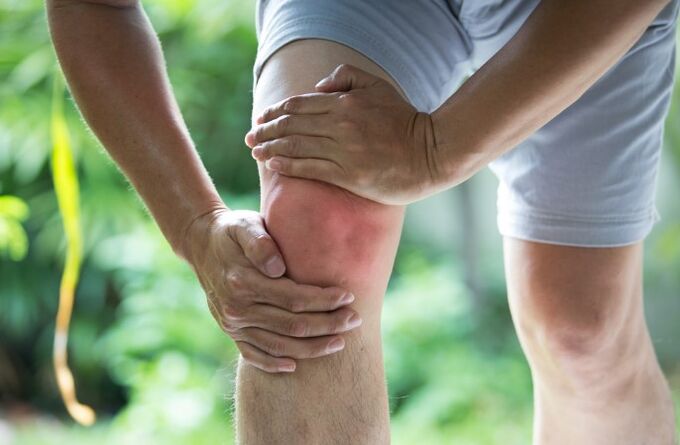
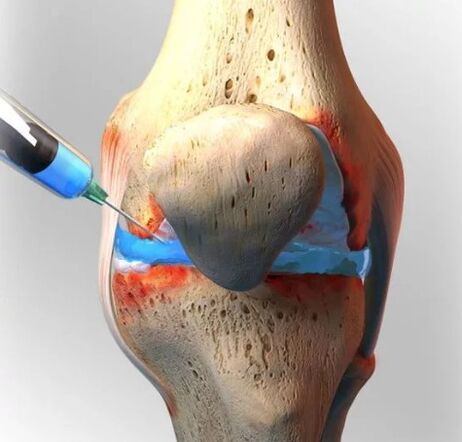
Everything you need to know about arthrosis - its causes, signs, varieties and diagnostic methods - will help to detect the disease in the early stages. And effective treatments will allow you to get rid of this disease. Arthrosis is characteristic of people over 40 years of age. However, impartial statistics have shown in recent decades a tendency to rejuvenate men and women aged 30-35 years have begun to suffer.
Arthrosis is a chronic joint disease, accompanied by pathological changes in hyaline cartilage, and subsequently in adjacent tissues, joint capsule and synovial sheath. The defeat is dystrophic and degenerative by nature, which leads to a change in the structure of the joint tissues, the loss of their functionality. In accordance with the data from the same statistics, arthrosis is subject to 12% of the total population of the planet. From 62% to 65% of all episodes of the disease fall for people over 60 years. Another 30-35% of cases of joint damage to this pathology are in patients aged 40-60 years. And about 3% are young people aged 20-40 years.
The danger of joint disease is manifested by the fact that it is practically not completely cured. Although when diagnosing the pathology in the early phase of progression, it helps to maintain the functionality of the joint.
Most often, cases of arthrosis lesion in such joints are diagnosed:
The disease is more characteristic of the female population -representatives of the female half of the population suffer from this pathology more often at old age. Interphalanic arthrosis occurs in women 10 times more often than in the male population. 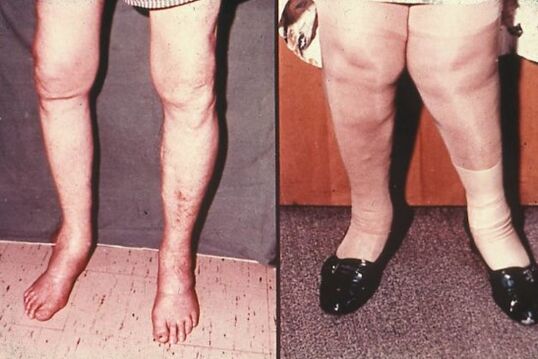
With timely treatment, the disease manifests itself from a lower intensity of development and as a result of this suspension of degenerative and dystrophic changes. This means that timely surgical or therapeutic intervention allows you to maintain your joint functionality, normal gait and eliminates soreness.
At the same time, tightening with treatment leads to frequent and stable pain, lame, swelling of the joint. Progressive pathological changes in the tissues deprive the joint of its usual functionality. For a short time, in the absence of competent treatment, arthrosis quickly goes into chronic form. Such consequences give rise to the need for constant medical monitoring and regular treatment of the disease during periods of exacerbation.
To avoid the consequences and complications with the first suspicions of its development, you should contact medical professionals. In the early stages of the progression of the treatment of arthrosis of the joints, the rheumatologist deals with treatment. In chronic form, the treatment of this pathology is performed by an orthopedic traumatologist.
This joint pathology has several forms and varieties that differ in such criteria:
At the site of the symptoms, the hip joint, the knee, the cyst, the elbow, the shoulder, the ankle, the arthrosis of the uterus of the cervix.
According to the etiological signs, pathologies of the primary nature are classified, developed without any prerequisites and secondary disease. In the latter case, the damage to the joint occurs due to the development of infectious diseases in adjacent tissues, mechanical disorders, loss of physiological functionality of the joint, as well as the result of a progressive inflammatory process, hypothermia, injury or other factors.
Localization classification includes local and generalized joint damage. In the first case, the disease and its symptoms cover a small portion of the joint or its individual tissues and components. In general, several joints are affected or one of them with full coating of all joint tissues.
At different stages of the progression of the disease, there is varying degrees of intensity. At the same time, the symptoms and complications can be expressed more brush, more or less dynamically leak the process of tissue destruction and impaired joint function.
Depending on the course of arthrosis, they distinguish: The acute form is usually manifested by increased intensity of the development of symptoms and their severity. The painful sensations occur more strongly and the morphological changes in the tissues are more dynamically. In chronic form, the course of the disease is slow, it is manifested by separate signs during periods of exacerbation and is practically not treated. During the disease, the drug distinguishes three stages that have differences in the signs of the disease, the intensity of the damage and the localization. At the same time, the distinction in all three stages refers to the types of tissues that undergo pathological changes. In addition to these three degrees of pathology development, there is a last stage - irrevocable destruction of all joint tissues. In this phase, it is impossible not only to perform productive therapy, but even to eliminate the pain syndrome. The inflammatory process usually begins with a second degree of damage, in rare cases in the absence of medical intervention - in the first stage. Subsequently, it becomes more difficult to stop and this can lead to secondary pathologies, the development of pathogenic microflora at the site of localization of the disease. In order to exclude serious consequences, treatment should start from first degree and the use of intensive care methods. At the last stage associated with the complete destruction of cartilage tissue, only one methodology for driving the patient from pain and immobility of the joint is allowed - endoprothetic with complete or partial replacement of the components of the joint. The reasons may be primary and secondary factors. In older people, the disease can occur in mixed etiology, that is, in the presence of primary and secondary causes. Their complex manifestation exacerbates the course of arthrosis and reduces the dynamics of recovery. The main cause of most species of this pathology is a violation of metabolism. Altered metabolic processes lead to morphological abnormalities in cartilage and synovial fluid. As a result, the changes refer to the whole joint and are often accompanied by the origin of inflammatory local foci. In addition to metabolic pathologies, the causes of joint arthrosis are: A separate place in the etiology of arthrosis is a genetic factor. It is the genetic anomaly that is able to cause dysplasia of joint tissue and disorder of the physiological functions of collagen fibers responsible for the flexibility and mobility of the joint. At the same time, other concomitant factors are the causes of the development of this pathology: vitamin deficiency, intoxication due to the quality of suction quality, or excessive drug overdose, the advanced age of the patient, the pathological processes of bloodstream and blood flow, hormone abnormalities and the disease of the reproductive system. When any of the causes that provoke the disease of the joint with arthrosis, pathological processes begin to develop. The mechanism of their progression has not been fully studied, but the main stages of official medicine are known. At the initial stage, the structure of cartilage tissue and abnormal changes in the synovial fluid appears. All this is done due to disorders of the metabolic processes in which joint tissues do not receive the necessary components in sufficient quantities or are deprived of some of them. Next, the elasticity of collagen fibers and the flexibility of cartilage are lost due to the fact that in the body, with a lack of nutrients, hyaluronic acid does not have time to produce, which provides the softness and flexibility of the structural composition of collagen fibers. The cartilage gradually dries, becomes brittle and cracks. The fluid in the synovial capsule gradually exhausted and subsequently disappears completely. Cartilage tissue is formed roughness, solid bone solama. At the same time, the deformity of other joint tissue, their pathological degeneration, dystrophy and loss of physiological activity develops. For the patient, these changes indicate the onset of pain, lame and immobility of the joint. Signs of arthrosis of the joints appear from its first degree, although sometimes they are not so pronounced. The characteristic phenomena for all stages of arthrosis are: Pain Pain usually occurs during movement. With intense physical activity, the painful sensations are enhanced and gain a constant trend. In all types of arthrosis, every place from their localization, the pain is acute. In the initial phase, the pain is poorly expressed, more often they appear during the day. Usually the pain is short -term and disappears at rest. In chronic form and with intense progression of the acute form of pain, pain syndrome is more common, there is an increased period of manifestation, often worried even at rest at night.